According to statistics, 30% of the adult population experiences periods of hypertension, which is almost always a sign of an independent pathology or so-called primary hypertension. Our country ranks 49th in the world in the number of patients with this disease.
Without treatment, complications of hypertension occur:
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- acute heart failure;
- hypertension crisis.
The insidiousness of the pathology is that in half of the cases patients do not even suspect that they have a dangerous disease, which is why they do not take any action and hypertension begins to manifest itself with unpleasant symptoms. Many countries have launched preventive programs that aim to combat the pathology. New, safe medications are being developed to control blood pressure levels. At the same time, only 1/3 of hypertensive patients undergo adequate therapy and take care of their health.
Doctors around the world believe that every home should have a device for measuring blood pressure, along with a thermometer. This is especially true for families whose relatives have previously suffered from cardiovascular diseases.
Causes of hypertension
Currently, the exact causes of hypertension have not been established. The main risk factor is prolonged or severe psycho-emotional stress. Other causes of pathology include:
- excess body weight: with excess weight, each kilogram increases blood pressure by two mmHg;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- eat canned foods, smoked meats, fatty foods, spicy cheeses;
- excessive use of salt in cooking;
- frequent stress;
- smoking - harmful substances contained in cigarettes contribute to mechanical damage to the walls of the arteries;
- busy work schedule;
- alcohol consumption;
- very tall or short stature in men;
- physical and nervous fatigue;
- consumption of animal proteins, which is not limited.
Risk factors also include hereditary predisposition. Hypertension in first-degree relatives guarantees a high risk of developing the disease.
It is worth paying attention to age, from the age of 35 onwards, men have a greater chance of acquiring the disease. In women, the pathology is associated with the onset of menopause.
Symptoms of hypertension
Often there are no signs of pathology, but sometimes the following symptoms can be observed:
- headache;
- fast or weak heartbeat;
- dizziness;
- swelling of the eyelids, legs and arms, swelling of the face;
- memory impairment;
- numbness of the fingers;
- facial redness;
- chills;
- increased sweating;
- anxiety;
- internal tension;
- decreased performance;
- irritability;
- the appearance of "mosquitoes" before the eyes.
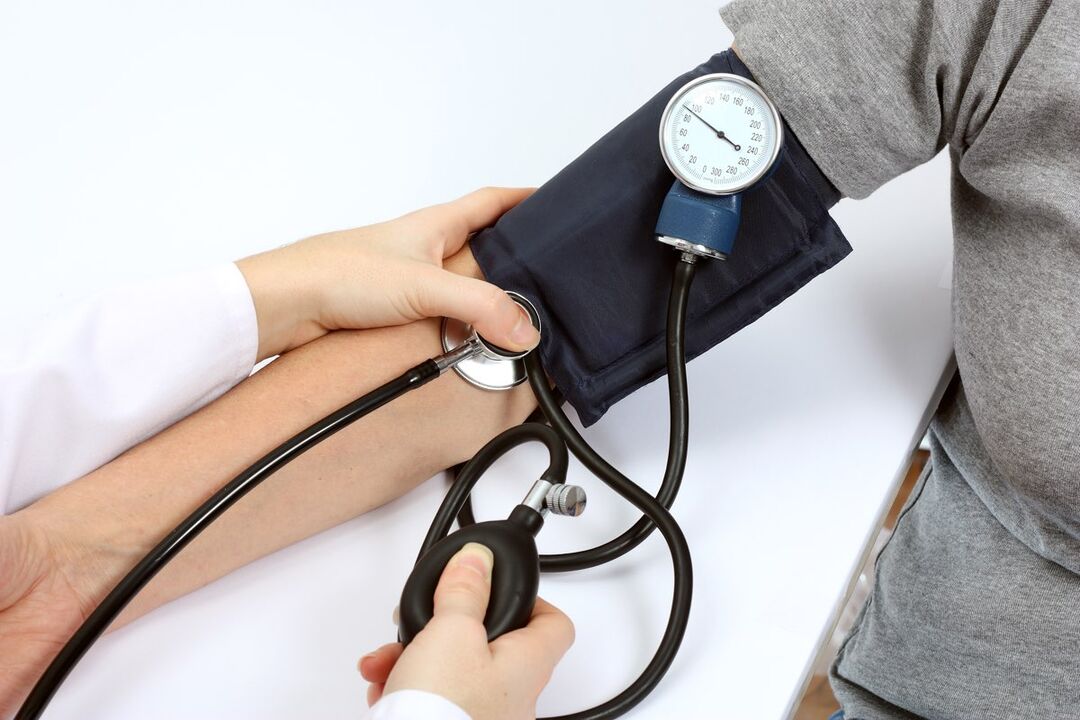
All these manifestations do not bother patients constantly, but occur only over a certain period of time. This is the insidiousness of the disease, therefore, if the above symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor for advice. If therapy is not started on time, over time the disease will begin to progress and can lead to serious complications. Therefore, it is important to control blood pressure. For this purpose, there are today many special tonometers, from conventional mechanical devices to fully automated models. The operation of tonometers with a stethoscope is more difficult, it is not always possible to distinguish the sounds of the pulse, but after some training and practice, almost everyone can learn this.
Before measuring blood pressure, you should not smoke, drink alcohol or coffee, it is advisable to rest for a few minutes. The measurement is carried out in a sitting position, the cuff should be fixed just above the elbow, where the pulse is best felt. Most often, aneroid (lever and inflatable type) and automatic devices are used to determine pressure. In an outpatient setting, devices are used that can monitor changes in pressure throughout the day.
Each age has its own blood pressure standards:
- 16-20 years – pressure 100/70 – 120/80;
- up to forty years of age the norm is 120/70 – 130/80;
- from forty to sixty – up to 135/85;
- After sixty years, normal blood pressure is considered up to 140/90.
In cases where the readings exceed the norm for several days in a row, this is a mandatory reason to consult a doctor, even if there are no symptoms other than the device data. A competent doctor will give lifestyle recommendations for early-stage hypertension, which will help avoid complications.
Hypertension - classification
During the study of the disease, several classifications with divisions were developed: by etiology, appearance of the patient, stability and level of pressure, reasons for the increase, nature of the course. Some of them are still used by doctors today.
The first classification of hypertension divided it into red and pale. The patient's appearance played a decisive role in this division. In the pale variety, the patient had cold extremities and an unhealthy complexion, which is explained by vasospasm. With red hypertension, when blood pressure rises, the patient's face, on the contrary, becomes red and covered with spots.
In practice, one of the most important classifications is the division of the disease by origin. There is a primary, or essential, form that occurs as an isolated pathology. At the same time, there are no diseases of other organs and systems.
The secondary form is a symptom of pathology of organs that participate in the regulation of vascular tone. These include the kidneys, endocrine and nervous systems.
There is no unified systematization of hypertension, but, as a rule, doctors use the classification recommended by the World Health Organization. It is characterized by the degree of increase in pressure.
- Stage 1 hypertension is a mild form, characterized by pressure of 140/90 to 159/99 mmHg.
- 2nd degree hypertension - moderate hypertension, pressure rises to 79/109 mm Hg. Art. Sometimes doctors diagnose "stage 2, risk 2 hypertension, " which means there are one or two risk factors and the possibility of complications has arisen.
- Hypertension of the 3rd degree is characterized by a severe course, the pressure rises to 180/110 mm Hg. Art. and even higher. If, upon examination, the doctor diagnosed "hypertension, stage 3, risk 4", it is necessary to immediately start treatment and seek help in a hospital. In this case, the probability of complications increases to 30%.
The organs most susceptible to complications from hypertension are:
- brain – DEP, dementia, strokes, memory loss;
- kidneys – development of chronic renal failure;
- heart - heart failure, heart attack, coronary death;
- vessels;
- eyes.
Doctors classify the disease according to the damage to the above organs. Stages of hypertension:
- Stage I – the functioning of the cardiovascular system is not impaired, patients generally do not complain about their condition.
- Stage II – enlargement of the left ventricle, increased blood pressure. Local narrowing of retinal vessels may be observed.
- Stage III - signs of organ damage appear: chronic renal failure, angina pectoris, hypertensive encephalopathy, disorders that an ophthalmologist can detect when examining the fundus (swelling of the optic nerve, hemorrhages), aortic aneurysm.
When classifying, options for increasing pressure are taken into account. In this case, the following forms are distinguished:
- diastolic – increase in lower pressure;
- systolic – only the upper indicators increase;
- systolic-diastolic;
- labile form - in this case, the pressure rises briefly and returns to normal without special medications.
There are certain types of hypertension that are not included in any of the classifications. These are refractory hypertension and hypertensive crises.
Refractory hypertensionIt is high blood pressure that is not corrected with medication. The pressure does not decrease even with the use of more than three medications. Sometimes this form of the disease is incorrectly diagnosed when medications are chosen incorrectly or even the diagnosis is incorrect.
Hypertensive crisis is a condition in which blood pressure rises to critical levels. Because of this, the patient experiences dizziness, severe headaches, impaired cerebral circulation and cerebral hyperthermia may occur.
Hypertension during pregnancy
In a healthy woman, blood pressure should remain within normal limits during pregnancy. However, from the 20th week onwards, some patients may develop pre-eclampsia, which occurs due to vasospasm. The result is increased blood pressure, bloating and nausea. In severe cases, high blood pressure threatens a stroke; this condition is dangerous for both the child and the woman.
Therefore, it is important for pregnant women to constantly monitor their blood pressure. If your blood pressure rises, you should inform your doctor, who will select an appropriate treatment for hypertension that is safe during this period.
If you notice similar symptoms, see your doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Diagnosis
Depending on the degree and stage of hypertension, treatment is selected. Before starting therapy, the doctor will certainly prescribe diagnostic tests that should confirm the presence of the disease.
Laboratory tests include: general blood and urine analysis, urine analysis according to Nechiporenko, biochemical blood test and bacterial culture.
The mandatory diagnostic program includes:
- clinical examination;
- take anamnesis;
- measure body weight and waist circumference;
- measure blood pressure in both arms;
- ECG and FCG;
- fundus examination.
Treatment of hypertension
Stage 1 hypertension, symptoms and treatment
Stage 1 hypertension is characterized by a periodic increase in pressure, which after some time returns to normal on its own. In this case, the patient may experience a headache, dizziness, tinnitus, and "spots" may flash before the eyes. At the first stage of the disease, the doctor will tell you how to treat hypertension without special medications. The patient needs to adjust their lifestyle, monitor their weight, stop drinking alcohol and smoking, exercise regularly, as well as review their diet and try to avoid stress and excessive physical exertion.
Treatment aids include: reflexology, massage, physiotherapy, herbal medicine.
Medicines are rarely prescribed, only in cases where other methods of therapy have proven ineffective and the disease has passed to the next stage of development.
Hypertension 2 degrees, symptoms and treatment
As a rule, the disease does not develop over a short period of time. Several years pass before hypertension progresses to stage 2. Symptoms of the pathology include:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- numbness in fingers and toes;
- fatigue;
- cardiopalm.
When a persistent increase in blood pressure occurs, the doctor prescribes special medications to treat hypertension. They must be used continuously, regardless of tonometer readings. It is recommended to take diuretics, which help remove excess fluid from the body.
In some cases, a decision is made to prescribe ACE inhibitors, which affect the narrowing of blood vessels. They can increase the effects of diuretics by reducing the ability to produce aldosterone.
Medicines that reduce blood viscosity are used, as well as medicines that reduce cholesterol levels.
A wide variety of medicines allows you to choose treatment individually for each patient. At the same time, do not forget about non-medicated and auxiliary means. Combined therapy gives positive results.
Hypertension 3 degrees, symptoms and treatment
A doctor can diagnose stage 3 hypertension when there is end-organ damage. Because today blood pressure levels can be successfully adjusted with medications, less attention is paid to the magnitude of blood pressure readings.
The reason for the development of this degree of the disease, in most cases, is late access to the doctor and lack of adequate treatment. Modern diagnostic capabilities make it possible to detect even the smallest changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Often patients themselves neglect the opportunity to visit a specialist. Taking medications (pills) for hypertension at certain stages of the disease helps to reach the level of physiological norm, not limited to "working blood pressure". This allows patients to avoid the third stage of the disease and significantly improve their quality of life.
Signs of organ damage are added to the symptoms of the disease. Most often, damage to blood vessels and structures of the central nervous system is diagnosed in the brain. The risk of myocardial infarction and development of hemodynamic instability increases significantly. The kidneys suffer, problems arise associated with damage to the retina.
It is important to understand that when organs are damaged, a vicious circle occurs. Emerging diseases worsen the course of hypertension and are difficult to treat.
As in other cases, treatment must consist of several stages. These are dosed physical activities and recreational activities. Patients need to maintain a work and rest schedule, establish a healthy diet and not forget about drug therapy.
Treatment of hypertension in the elderly
Elderly people suffering from this disease constitute a separate group of patients who require a special approach to treatment. Drug lowering blood pressure in the elderly has its own characteristics.
Standard therapy is not always suitable for patients over 60 years of age, but this is not a reason to abandon treatment. Here it is important to individually select effective medicines and tune in to a positive result.
If the elderly person does not present any complications, it is recommended to start treatment with a thiazide diuretic. Their effectiveness increases with the patient's age, so after the age of 55 these medications are much more effective than at an earlier age. It is important to remember that diuretics are prescribed in small doses, as increasing them can cause an increase in cholesterol. If a patient has low potassium or sodium levels, potassium-sparing agents are recommended.
If the patient, for objective reasons, cannot take diuretics, beta-blockers become the medication of choice.
In the low-renin form of hypertension, calcium antagonists are prescribed to support cerebral and renal blood flow. Additionally, these medications are effective remedies for angina pectoris and can reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers and ACE inhibitors are not as effective as the above medications, but can be used when other medications do not provide the desired effect. Strong medications are rarely prescribed because they cause drowsiness, depression, and low blood pressure, even when standing.
It has been proven that combined medications for the treatment of hypertension reduce blood pressure more effectively than a single medication in an increased dosage. Therefore, in modern medicine, drug combinations are prescribed:
- diuretic and calcium antagonists;
- beta blockers with diuretics;
- ACE inhibitor with calcium antagonist;
- ACE inhibitor diuretic.
When a hypertensive crisis occurs, the patient requires rehabilitation. Usually this problem is solved in a sanatorium. The following measures are recommended for patients:
- physiotherapy;
- dietary nutrition;
- medicinal baths;
- hardware physiotherapy;
- Phytotherapy;
- aromatherapy;
- oxygen cocktails;
- drug treatment courses.
As maintenance therapy, patients are recommended to use electrosleep, laser therapy and electrophoresis. Thanks to electrical impulses, blood pressure decreases and the kidneys and heart become healthier.
With the help of sulfide and carbon dioxide baths, the functioning of the immune system improves and blood pressure normalizes. The choice of procedures is determined by the patient's age and the stage of the disease.
Folk remedies in treatment
Treatment of hypertension should be comprehensive, along with traditional dosage forms, you can use traditional medicine, which contains many effective recipes.
- Red clover decoction. The plant is prepared in the same way as regular tea and consumed half a glass at night. It is advisable to use only fresh decoction, but you can store the medicine in the refrigerator for up to three days.
- Honey and garlic. You need to take half a glass of honey, crush five cloves of garlic and grind one lemon together with the peel. Mix everything well and place in a dark place for a week, after which the composition must be stored in the refrigerator, in a closed container (you can wrap it in a cloth or foil). Take one teaspoon three times a day.
- Vegetable juices. Mix a glass of carrot, black radish and beetroot juice with a glass of honey and juice of one lemon. Take one tablespoon three times a day before meals. The duration of the course is one and a half months.
- Rosehip infusion can be drunk without restrictions.
- Seeds. Pour well-washed and shelled sunflower seeds into the pan. Pour one and a half liters of cold water and boil for about two hours over low heat. The broth must be strained and drunk a glass throughout the day.
- Golden mustache. Finely chop the dark purple knee and pour 0. 5 liters of vodka. Leave for twelve days in a dark place, gently shaking the contents every three days. Take a dessert spoon half an hour before meals.
- Lemon: Mix 1 glass of white onion juice and 1 glass of honey and add 50 grams of pre-crushed lemon peel. Close the container where the infusion will be stored tightly and place it in a dark place. Take the infusion one teaspoon after meals, two to three hours later. Or mix a tablespoon of grated lemon 1: 1 with chopped cranberries, add half a tablespoon of fresh rosehip (you can grind it in a meat grinder). Add the mixture to a glass of honey and take a tablespoon morning and night.
- Honey. Mix five hundred grams of May honey with half a liter of vodka and heat until foam appears. In this case, the mixture must be constantly stirred. Let it ferment. For the second composition, you need to prepare a pinch of the following herbs in a liter of water: chamomile, cudweed, valerian, knotweed, motherwort. Let the broth ferment, then strain and mix with the first mixture. Place the tincture in a dark place for three days. In the first week, the composition is taken twice a day, one teaspoon, the next week, one tablespoon, until the broth runs out. Treatment in this way is long-term, with intervals of 7 to 10 days.
Diet for hypertension
Proper and balanced nutrition for hypertension is the key to success in combating the disease. It is worth remembering that each extra kilo increases the tonometer numbers. The main task is to achieve the ideal weight if it does not meet the standards. To normalize blood pressure, the following recommendations must be followed.
- Reduce your salt intake. As sodium retains water in the body, the volume of circulating blood increases, which affects the increase in blood pressure. The amount of salt will be about 4 grams. Ideally, there is no need to add additional salt to food during cooking.
- To normalize metabolism, you need to drink plenty of fluids, about 1. 5 liters per day. It is necessary to give preference to clean water, rosehip broth, as well as "healthy" soups.
- Eliminate coffee, strong tea and alcohol from your diet.
- Fractional meals. It is important to distribute your diet so that you eat equal portions five to eight times a day.
- Reduce the amount of meat and animal fats you consume. Patients are advised to choose lean meats - turkey, veal, chicken, rabbit. It is best to cook without oil, if the meat seems bland, you can add herbs and lemon juice to replace the salt. You should include smoked meats, sausages and butter in your diet as rarely as possible.
- It is important to increase the amount of vegetables and foods rich in potassium and magnesium consumed: cereals, beets, carrots, dried apricots, cabbage.
- It is recommended to avoid the consumption of confectionery products with a high sugar content, giving preference to dried fruits, honey and whole grain products.
- Patients with hypertension should not fast. Strict fasting and diets are contraindicated.
Disability due to hypertension
Hypertension is a serious disease and in some cases patients are considered disabled. It is generally administered to patients with second or third stage disease or constant progression.
In the case of stage 1 hypertension, the labor medical commission must assist with employment, as increased stress, night work and work associated with contact with dangerous substances must be avoided.
When determining disability, a special medical commission evaluates disabilities, the presence of complications and the history of hypertensive crises. Sometimes, already in the second stage of hypertension, the third group can be diagnosed.
Deficiency of the second group can be obtained by patients with malignant disease, in most cases it is inoperative.
In patients with grade 3 hypertension, the first group of disability can be established in the case of:
- constant progression;
- severe heart failure;
- serious disturbances in the functioning of organs;
- the patient is unable to care for themselves and has limited movement and communication.
Prevention of hypertension
Primary prevention should eliminate risk factors that contribute to the occurrence of hypertension:
- maintain normal body weight;
- limit the use of table salt;
- elimination of bad habits - smoking, alcohol;
- try to avoid physical and nervous stress;
- prevention of physical inactivity;
- treatment of chronic diseases.
Secondary prevention consists in the selection of drugs that stabilize blood pressure, as well as the choice of a set of supportive measures.